Market Research
Building Trust Through Cybersecurity and Privacy

KPMG has released its “Cyber trust insights 2022” report that analyses the five crucial steps to building trust through cybersecurity and privacy. The report surveyed 1,881 executives and conducted a series of discussions with corporate leaders and professionals worldwide to explore the extent to which the C-suite recognizes this, how they are meeting the challenge and what they need to do next.
KPMG says it has identified five crucial steps toward building trust through cybersecurity:
- Treat cyber and privacy as a golden thread woven into the business
- Build internal alliances
- Reimagine the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO role
- Secure leadership support
- Reach out to the ecosystem
Emerging technologies such as distributed ledger technology (DLT), quantum computing, 5G networks, artificial intelligence (AI)/machine learning (ML), and augmented and virtual reality are developing rapidly and promise to transform how businesses operate. However, the successful rollout of future applications (connected economy, smart systems, NFT, metaverse, etc.) that rely on these technologies will likely be governed by an organization’s ability to instill trust across multiple dimensions. This means embedding security and privacy controls with transparency, reliability, and integrity, the report said.
Organizations know they must become data-driven or risk irrelevance. Many are scaling AI to automate data-driven decision-making, but AI brings new risks to brands and profitability. The technology has the potential to drive inequality and violate privacy, as well as limit the capacity for autonomous and individual decision-making.
“You can’t simply blame the AI system itself for unwanted outcomes. Trustworthy, ethical AI is not a luxury, but a business necessity. Growing numbers of business leaders recognize this, but trust is not secured without effort or challenges,” stated Ton Diemont, Head of Cybersecurity and Data Privacy at KPMG in Saudi Arabia and the Levant.
He stated that trustworthy AI can only be achieved with a holistic, technology-agnostic, and broadly endorsed approach to awareness, AI governance, and risk management. Globally, the growth of cybersecurity and privacy regulation is accelerating. More than 137 countries now have some form of data-protection regime, often claiming extra-territorial jurisdiction over services offered in the country or the data of citizens of that country.
More mature privacy regimes are moving into the second generation of regulation while confronting new privacy challenges driven by technology adoption, Diemont said, indicating discussions about the regulation of AI are now being formalized in the draft legislation. In addition, countries are implementing increasingly strict critical infrastructure cybersecurity regulations as concerns grow around attacks on industrial control systems. These regulations move from self-assessment to more directive control frameworks, including mandatory incident reporting and external audits.
Regulators are also being more prescriptive in their control frameworks, while also seeking to reinforce the independence of the CISO and their role in setting internal control standards, the report stated. Corporate requirements for transparency over cyber risks are under debate, along with growing requirements for the disclosure of ransomware incidents. Companies should invest in automating compliance monitoring and reporting; maintain a regulatory watch, and consider privacy and security regulatory trends when developing new services and products, advised Diemont.
Organisations embracing the ESG agenda can earn their customers’ trust and reinforce their brands’ strength. In today’s digital world, boardrooms, investors, regulators, customers, and the wider public expect transparent reporting on the organization’s cybersecurity and privacy posture. Stakeholders want to feel confident that boards and executives appreciate the social implications of striving to ensure the resilience and integrity of critical services while protecting the information they hold in trust.
In the KPMG Cyber trust insights 2022 survey, almost half of the respondents (44 percent) say that collaboration on cybersecurity across the broader ecosystem will help them anticipate attacks. Although collaboration may be desirable, it’s not always straightforward. More than one-third of respondents (38 percent) say that privacy concerns stand in the way of external cybersecurity partnerships, and 36 percent worry about revealing too much about their own security arrangements. Other problems include regulatory restrictions, lack of support from the C-suite, and lack of resources.
According to the KPMG report, CISOs are now in a position to play a crucial role as enablers. By operating as one of the organization’s ultimate guardians of trust, it can be a driving force for its success. “CISOs themselves recognize what is at stake,” Diemont noted, adding more than three-quarters of respondents (77 percent) say increased trust is a key objective of their cyber risk programs.
Forty-five percent of C-suite respondents now see the CISO as a key executive and the profile of the CISO role has grown rapidly over the last five years, driven by digital transformation, growth in cybercrime, and rising regulatory expectations, he stated.
Market Research
Access Control and Data Exposure Flaws Prevalent in Corporate Web Apps: Kaspersky

A recent study by Kaspersky Security Assessment experts has identified the most dangerous and widespread vulnerabilities in corporate web applications developed in-house. In the period between 2021 and 2023, flaws related to access control and data protection were found in the majority of the examined applications, totalling several dozen. The highest number of high-risk level vulnerabilities referred to SQL injections.
Web applications like social networks, email, and online services are websites where users engage with a web server via a browser. In its latest study, Kaspersky researched vulnerabilities in web applications used by IT, government, insurance, telecommunications, cryptocurrency, e-commerce, and healthcare organizations to identify the most prevalent types of attacks that are likely to occur to enterprises.
The predominant types of vulnerabilities involved the potential for malicious use of access control flaws, and failures in protecting sensitive data. Between 2021 and 2023, 70% of the web applications examined in this study exhibited vulnerabilities in these categories.
A broken access control vulnerability can be used when attackers try to bypass website policies that limit users to their authorized permissions. This can lead to unauthorized access, the alteration, or deletion of data, and beyond. The second common type of flaw involves the exposure of sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, health records, personal data, and confidential business information, highlighting the need for increased security measures.
“The rating was compiled by considering the most common vulnerabilities in web applications developed in-house in various companies and their level of risk. For instance, one vulnerability could enable attackers to steal user authentication data, while another could help execute malicious code on the server, each with varying degrees of consequences for business continuity and resilience. Our rankings reflect this consideration, drawing from our practical experience in conducting security analysis projects,” explains Oxana Andreeva, a security expert at the Kaspersky Security Assessment team.
Kaspersky experts also looked at how dangerous the vulnerabilities in the groups listed above were. The largest proportion of vulnerabilities posing a high risk were associated with SQL injections. In particular, 88% of all the analyzed SQL Injection vulnerabilities were deemed to be high-risk. Another significant share of high-risk vulnerabilities was found to be linked with weak user passwords. Within this category, 78% of all vulnerabilities analyzed were classified as high-risk.
It is important to note that only 22% of all the web applications the Kaspersky Security Assessment team studied had weak passwords. One possible reason is that the apps included in the study sample may have been test versions rather than actual live systems.
Cyber Security
CrowdStrike Outs its Global Threat Report for 2024

CrowdStrike has announced the findings of the 2024 CrowdStrike Global Threat Report, highlighting a surge in adversaries leveraging stolen identity credentials to exploit gaps in cloud environments and maximize the stealth, speed and impact of cyberattacks. The report also details the biggest threats on the horizon for 2024, including the disruption of global elections and the exploitation of generative AI to lower the barrier of entry and launch more sophisticated attacks. In the 10th annual edition of the company’s seminal report, CrowdStrike highlights activity from some of the 230+ prolific threat groups that it tracks today.
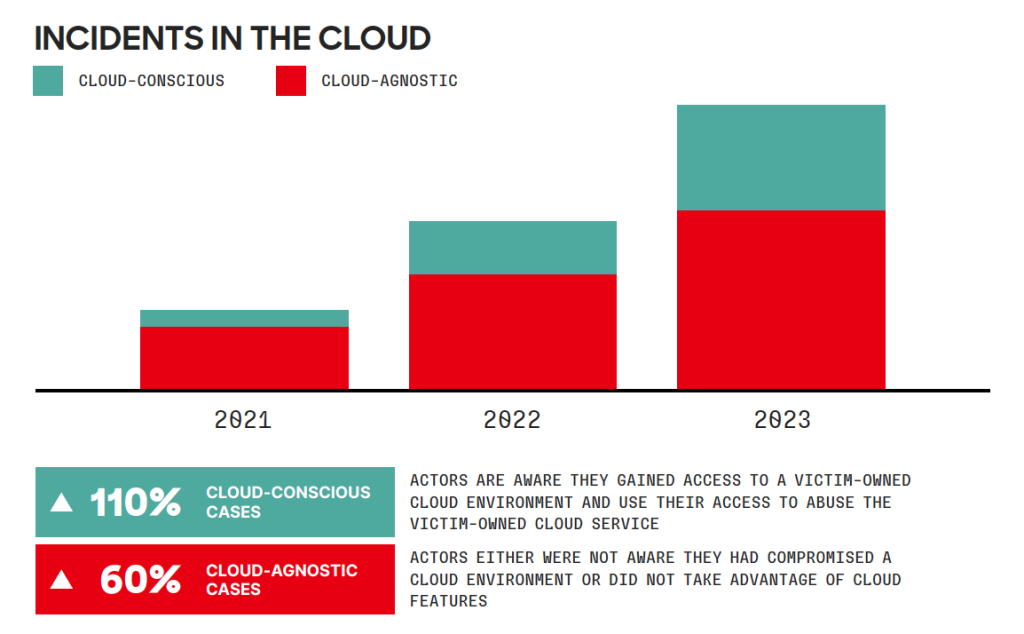
Key findings in the 2024 report include:
- Dramatic Increase in Attack Velocity: The speed of cyberattacks continues to accelerate at an alarming rate. The report indicates that the average breakout time is down to only 62 minutes from 84 in the previous year (with the fastest recorded attack coming in at 2 minutes and 7 seconds). Once initial access was obtained, it took only 31 seconds for an adversary to drop initial discovery tools in an attempt to compromise victims.
- Stealthy Attacks Spike as Adversaries Compromise Credentials: The report notes a sharp increase in interactive intrusions and hands-on-keyboard activity (60%) as adversaries increasingly exploit stolen credentials to gain initial access at targeted organizations.
- Adversaries Follow as Business Moves to the Cloud: Adversaries turned their sights to the cloud through valid credentials – creating a challenge for defenders looking to differentiate between normal and malicious user behaviour. The report shows cloud intrusions increased by 75% overall with cloud-conscious cases amplifying by 110% Year-over-Year.
- The Exploitation of Generative AI on the Horizon: In 2023, CrowdStrike observed nation-state actors and hacktivists experimenting with and seeking to abuse generative AI to democratize attacks and lower the barrier of entry for more sophisticated operations. The report highlights how generative AI will likely be used for cyber activities in 2024 as the technology continues to gain popularity.
- Disrupting Democracy by Targeting Global Elections: With more than 40 democratic elections scheduled in 2024, nation-state and eCrime adversaries will have numerous opportunities to disrupt the electoral process or sway voter opinion. Nation-state actors are highly likely to conduct mis-or disinformation operations to sow disruption against the backdrop of geo-conflicts and global elections.

“Throughout 2023, CrowdStrike observed unprecedented stealthy operations from brazen eCrime groups, sophisticated nation-state actors and hacktivists targeting businesses in every sector spanning the globe. Rapidly evolving adversary tradecraft honed in on both cloud and identity with unheard-of speed, while threat groups continued to experiment with new technologies, like GenAI, to increase the success and tempo of their malicious operations,” said Adam Meyers, head of Counter Adversary Operations, CrowdStrike. “To defeat relentless adversaries, organizations must embrace a platform approach, fueled by threat intelligence and hunting, to protect identity, prioritize cloud protection, and give comprehensive visibility into areas of enterprise risk.”
Cyber Security
Cyber Adversaries Using Analytics to Measure “Victims per Click”

HP has issued its quarterly HP Wolf Security Threat Insights Report, showing attackers are continuing to find innovative ways to influence users and infect endpoints. The HP Wolf Security threat research team uncovered several notable campaigns including:
- DarkGate campaign uses Ad tools to sharpen attacks: Malicious PDF attachments, posing as OneDrive error messages, direct users to sponsored content hosted on a popular ad network. This leads to DarkGate malware.
- By using ad services, threat actors can analyze which lures generate clicks and infect the most users – helping them refine campaigns for maximum impact.
- Threat actors can use CAPTCHA tools to prevent sandboxes from scanning malware and stopping attacks by ensuring only humans click.
- DarkGate hands backdoor access to cybercriminals into networks, exposing victims to risks like data theft and ransomware.
- A shift from macros to Office exploits: In Q4, at least 84% of attempted intrusions involving spreadsheets, and 73% involving Word documents, sought to exploit vulnerabilities in Office applications – continuing the trend away from macro-enabled Office attacks. But macro-enabled attacks still have their place, particularly for attacks leveraging cheap commodity malware like Agent Tesla and XWorm.
- PDF malware is on the rise: 11% of malware analyzed in Q4 used PDFs to deliver malware, compared to just 4% in Q1 and Q2 2023. A notable example was a WikiLoader campaign using a fake parcel delivery PDF to trick users into installing Ursnif malware.
- Discord and TextBin being used to host malicious files: Threat actors are using legitimate file and text-sharing websites to host malicious files. These sites are often trusted by organizations, helping the sites to avoid anti-malware scanners, increasing attackers’ chances of remaining undetected.
Alex Holland, Senior Malware Analyst in the HP Wolf Security threat research team, commented, “Cybercriminals are becoming adept at getting into our heads and understanding how we work. For instance, the design of popular cloud services is always being refined, so when a fake error message appears, it won’t necessarily raise an alarm, even if a user hasn’t seen it before. With GenAI generating even more convincing malicious content at little-to-no cost, distinguishing real from fake will only get harder.”
By isolating threats that have evaded detection tools on PCs – but still allowing malware to detonate safely – HP Wolf Security has specific insight into the latest techniques used by cybercriminals in the fast-changing cybercrime landscape. To date, HP Wolf Security customers have clicked on over 40 billion email attachments, web pages, and downloaded files with no reported breaches.
The report details how cybercriminals continue to diversify attack methods to bypass security policies and detection tools. Other findings include:
- Archives were the most popular malware delivery type for the seventh quarter running, used in 30% of malware analyzed by HP.
- At least 14% of email threats identified by HP Sure Click bypassed one or more email gateway scanners.
- The top threat vectors in Q4 were email (75%), downloads from browsers (13%) and other means like USB drives (12%).
Dr. Ian Pratt, Global Head of Security for Personal Systems at HP Inc., commented, “Cybercriminals are applying the same tools a business might use to manage a marketing campaign to optimize their malware campaigns, increasing the likelihood the user will take the bait. To protect against well-resourced threat actors, organizations must follow zero trust principles, isolating and containing risky activities like opening email attachments, clicking on links, and browser downloads.”
-

 Cyber Security6 days ago
Cyber Security6 days agoCheck Point Announces a New Collaboration with Microsoft
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoCloudflare Acquires Baselime
-

 Cyber Security6 days ago
Cyber Security6 days agoSophos Partners with Tenable to Launch New Sophos Managed Risk Service
-

 GISEC4 days ago
GISEC4 days agoBotGuard OÜ to Launch ALB for Hosting Providers at GISEC 2024
-

 GISEC2 days ago
GISEC2 days agoSANS Institute to Put the Spotlight on AI Security at GISEC 2024
-

 Cyber Security1 day ago
Cyber Security1 day agoMilestone Systems Releases Thought Paper on Cybersecurity for Video Technology
-

 GISEC21 hours ago
GISEC21 hours agoSectigo to Focus on Automated CLM Solutions at GISEC 2024
-

 GISEC2 days ago
GISEC2 days agoSolarWinds to Showcase Hybrid Cloud Observability at GISEC 2024

























